
What is Natural Vegetation Of India?
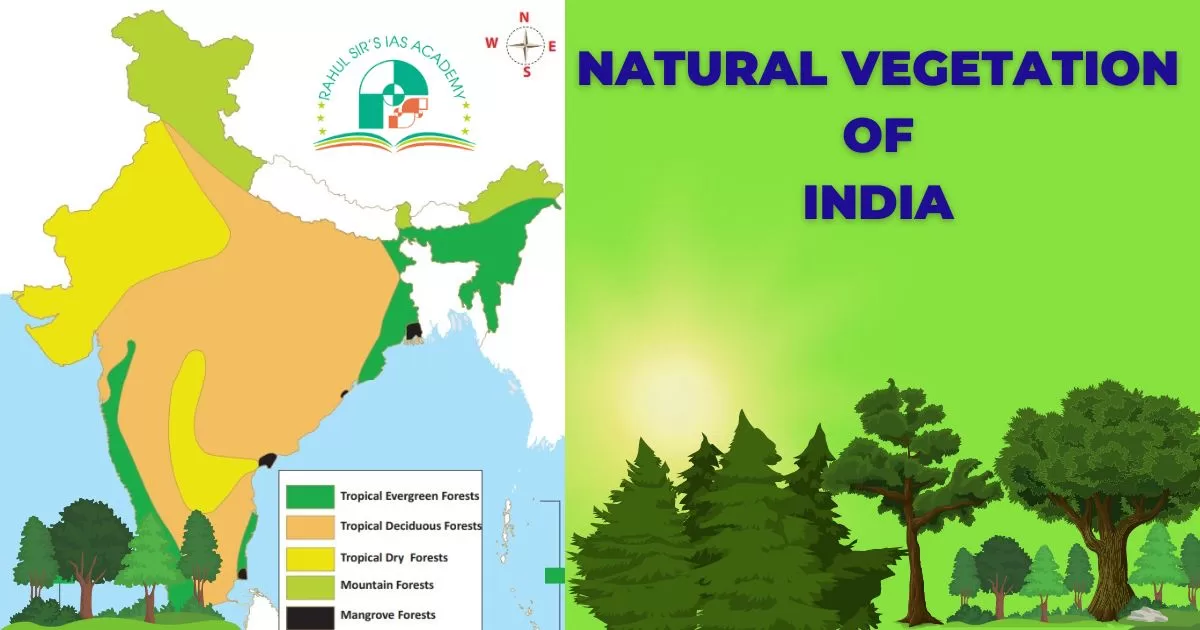
Natural vegetation of India is perfectly in tune with its relief and climatic conditions. The natural vegetation of India has a long history as many species of trees have migrated from one place to another due to tectonic and geologic reasons. Since India presents a greater varsity of physiographic and climatic conditions, it has an equally varied vegetation. Precipitation and temperature are the major determining factors for the distribution of natural vegetation in the country. The whole of Indian vegetation can be classified into five major categories. These can be seen as:
Tropical Evergreen or Rain Forest Type
Tropical evergreen forests are mainly found in the areas recording over 150 cm of average annual rainfall where the temperature varies between 25°C to 27°C. North-East India, parts of Western Ghats, the Andaman and Nicobar, upper Assam, lower slopes of Eastern Himalayas, Odisha, along the foot-hills of Himalayas, Bhabhar and Tarai regions. Wherever the average annual rainfall is more than 250 cm, these forests are dense and composed of tall trees (45 m) epiphytes, parasites, lianas and rattans. Because of this they appear like a green carpet when viewed from above.
Trees of tropical evergreen forests have multi-storeyed structures with good canopies. These trees do not shed their leaves annually and are hence evergreen. Thus they are not deciduous. The floor lacks grasses because of deep shade (sunlight cannot reach the ground). There are, however, canes, palms, bamboos, ferns, and climbers which make passage difficult. The important species of these forests are white cedar, toon, dhup, palaquium, mesua, caulophyllum, hopea, and canes, gurjan, chaplas agor, muli, and bamboo. Due to poor accessibility these forests have not been properly exploited.
These are further subdivided into three categories on the basis of rainfall:
1. Tropical Wet Evergreen Forest
These are well developed in areas receiving more than 240 cm of rainfall and a short dry season. Striped along the Sahyadris up to 1370 meter, the hilly regions of North-east India, the Terai region of eastern Himalaya and the Andaman and Nicobar islands have evergreen forests. Very dense forests having three storeyed appearance , composed of tall and medium sized trees and shrubs . Rosewood, Eboni, Ironwood and Paan are important trees. Toon, Sisso, Gurjan, Champa and Telsur are other important trees.
2. The Tropical Semi-Evergreen Forest
In areas of 200 cm of rainfall, found along the margins of wet evergreen forest.
3. Tropical Moist-Deciduous Forest
These are typical monsoon forests found in the areas of Western Ghats, Eastern Ghats , Chota Nagpur plateau , M.P. and the Bhabar and Tarai regions of the Himalaya receiving 100-200 cm. Rainfall. Open forests, Sal , Teak and Sandalwood are trees of economic importance. Here teak and sal are the dominant species. The tropical moist deciduous forests are found in Sahyadris, the north-eastern parts of the peninsula and along the foothills of the Himalayas.
These forests on the whole have gregarious species. The typical landscape consists of tall teak trees with sal, bamboo, and shrubs growing fairly close together to form thickets. Both teak and sal are economically important and so are the Sandalwood Shisham, Hurra and Khair.
Dry tropical Types
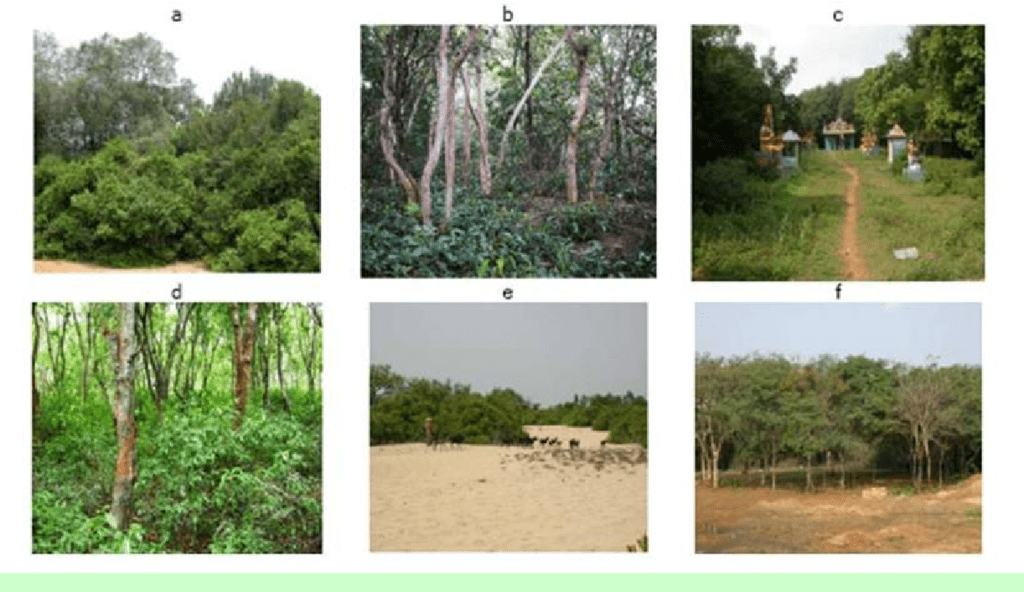

Occurs in areas of 75-125 cm of rainfall and subdivided into three types.
1. Tropical Dry Deciduous
Biotic variation of moist deciduous forests degenerating on the drier side into thorny forests , occurs over large areas of Sahyadris. Teak, Tendu, Sal , Palm , Laurel , Khair are important trees. These forests are characterized by closed and rather uneven canopies. Enough light reaches the ground to permit the growth of grasses and climbers. Acacia, jamun, modesta, and pistacia are the main trees. Grasses and shrubs appear during the season of general rains.
2. The Tropical Dry Evergreen Forests
They are confined to the coastal areas of Andhra Pradesh and Tamilnadu, because these areas receive 100 cm of rainfall mostly during winter through North-east monsoon. Neem, Tamarind, Palm , Casuarina, are important trees.
3. Tropical Thorn Forest
Occurs in low rainfall ( less than 75 cm) regions of Rajasthan and Gujarat. Stunted trees like Acacia are common with scrubs and xerophytic bushes in the drier side. Such forests also occur in the interior regions of the peninsula, having the rain-shadow effect of western Ghats.
Montane Vegetation of India
Montane vegetation of India can be broadly divided into 2 categories – Himalayan Vegetation and Peninsular Vegetation
Himalayan Vegetation
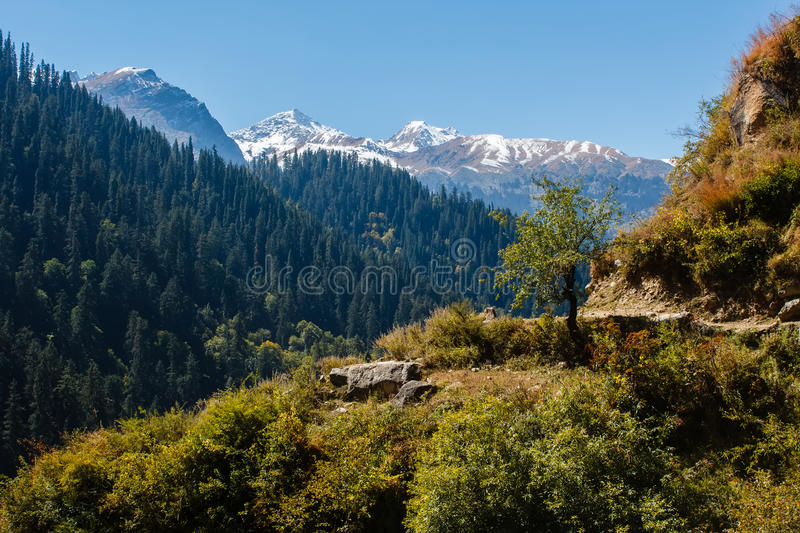

The Himalayan vegetation is further classified as Tropical, Temperate and Alpine mainly on the basis of altitude and rainfall.
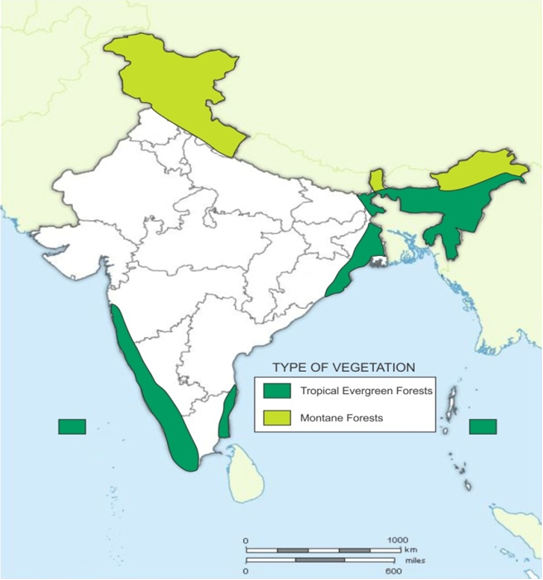
1. Tropical Evergreen Montane Forest
Tropical evergreen montane forest is confined to the humid foothills of eastern and central Himalayas up to a height of 1500 meter. Ironwood, oak, chestnut bamboos etc are found in these forests. In the western Himalayas rainfall decreases and evergreen forests give way to tropical deciduous forests , where the valuable timber tree sal is the dominant species.
2. Temperate Montane Forests
Temperate montane forests are formed at altitudes between 1500-3500 meter containing conifers and broad leaved temperate trees. These forests are found in the entire Himalayas from Jammu and Kashmir to Arunachal Pradesh between the altitudes of 1500 m to 3500 m where the temperature varies between 12°C to 15°C, and the mean annual rainfall is between 100 to 250 cm. Oak, fir, spruce Picea, deodar, magnolia , chestnut, cedar and maple, spruce, deodar, silver-fir , kail and yew are found here. These forests also contain scrubs, creepers, and ferns. The woods of these forests are durable. At higher altitudes above 3500 m, are the alpine pastures known as Margs in Kashmir and Bugyals in Uttarakhand. Pine is the dominant species at 920-1640 meter altitude. Deolar, a highly valued species, grows mainly in the western part of the Himalayan range up to 2700 meters.
3. Alpine Montane Vegetation
The alpine zone begins above the tree line at an altitude of 3200-3500 meter, extending up to 3900 meter in the western Himalayan. Juniper, Rhododendron, mosses and lichen are typical vegetation. These areas are characterized with short dwarf conifers and lush green nutritious grasses during the summer season. The trees found in the zone are kail, spruce, yew, firs, birch, honeysuckle, artemisia, potentilla, and small scrubs
Peninsular Montane Vegetation
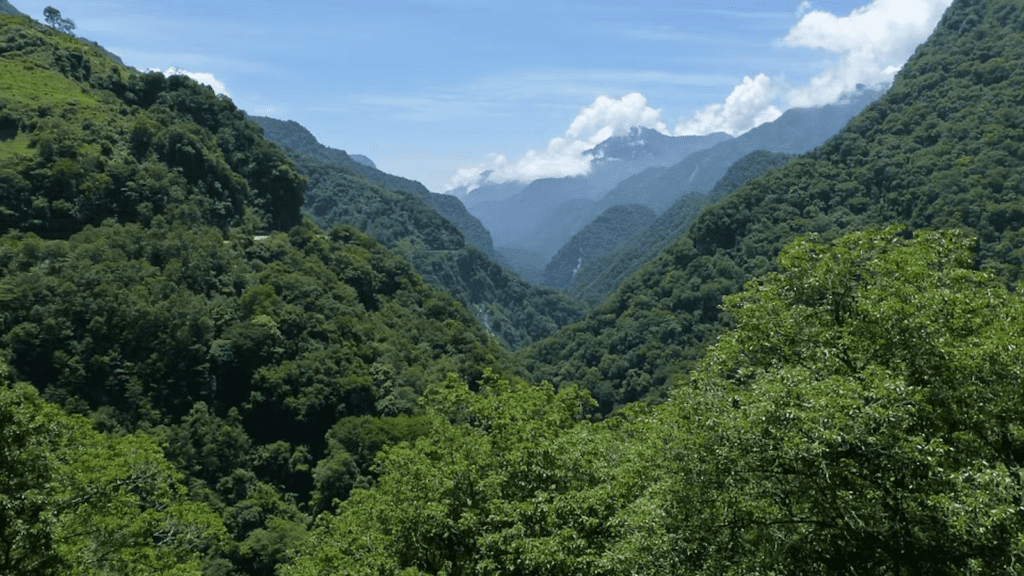

The subtropical forest occur on the lower slopes of Sahyadris and in Satpura and Maikal range . At higher levels the temperature is lower but rainfall is higher, therefore temperate forests are denser and called as Sholas in the Nilgiri, Annamalai, and Palani hills. Mongolia, Laurel, Rhododendron, Eucalyptus, Cinchona are found in this forest.
Tidal Forest
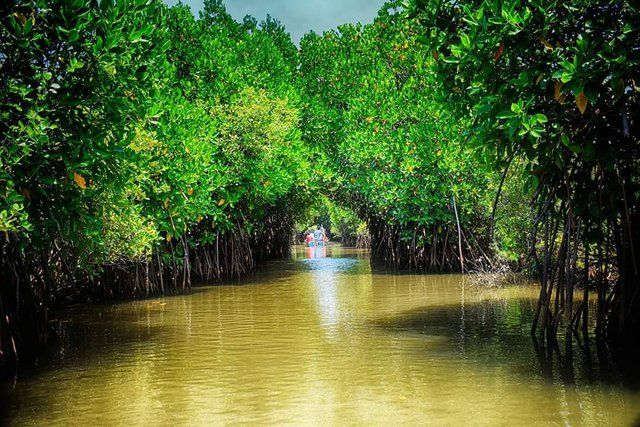

In the tide washed coast dense mangrove forests flourish with peculiar edaphic adaptations. The seaward fringes and island of the deltas of the Ganga, Mahanadi, Krishna and Godavari are belt of dense tidal forest. The great sundarbans is a typical example, inhabited by sundari trees. Their main concentration is found in areas where tides are frequent. Some mangroves attain a height up to 30 meters and are the most important trees commercially. It is utilized for fuel. At Sundarbans higher grounds support screw pines. Palms occupy creeks, and epiphytes are predominant all over the region.
Desert Vegetation (Natural Vegetation Of India)

The desert vegetation is confined to the west of Aravallis in the states of Rajasthan and northern part in Gujarat. The average annual rainfall in this area is less than 50 cm, the diurnal and annual range of temperature are high. Acacia, cacti, jhar and khejra, kanju, and wild palms are the main trees of the desert.
Natural Vegetation of India UPSC
Natural vegetation of India UPSC preparation has to be tackled in a systematic manner otherwise a candidate would end up loosing a lot of time in studying unnecessary things. In both prelims and mains questions from natural vegetation of India are asked on a regular basis. In mains also questions on this topic are asked. But to tackle a mains answer, pure knowledge is not enough. For this an answer writing skill is also required in which the placement of right keywords at right places is very important.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the natural vegetation of India is a remarkable treasure that needs to be protected, valued, and managed sustainably for the benefit of present and future generations. It is an integral part of India’s identity, supporting ecological integrity, cultural heritage, and the well-being of its people. Thus the natural vegetation of India is diverse and plays a crucial role in the country’s ecological balance and cultural heritage. From the towering evergreen forests of the Western Ghats to the arid shrublands of the Thar Desert, India showcases a remarkable range of plant species and ecosystems.
The country’s natural vegetation can be broadly classified into various types, including tropical rainforests, deciduous forests, thorn forests, alpine vegetation, mangroves, and grasslands. Each of these vegetation types harbors a unique assortment of flora and fauna, contributing to India’s rich biodiversity.
The natural vegetation of India not only supports a vast array of plant species but also provides habitat for numerous animal species, including endangered and endemic ones. These ecosystems serve as breeding grounds, migration routes, and sources of food and shelter for wildlife. They are essential for maintaining the balance of nature and ensuring the survival of many species.
Furthermore, the natural vegetation of India has immense cultural significance. Forests and trees hold a special place in Indian traditions, folklore, and spirituality. They are revered as sacred entities and are closely associated with various festivals, rituals, and customs. The indigenous communities residing in forested regions have deep-rooted connections with the natural vegetation, depending on it for their livelihood, medicinal resources, and cultural practices.
FAQs On Natural Vegetation Of India
Vegetation refers to the entire gamut of Kingdom Plantae. Natural vegetation is that part of plant kingdom that has no human interference. On the other hand the plantations, orchards, vineyards etc. are parts of vegetation but not natural vegetation.
Natural vegetation of India can be categorized in to 5 broad types – Tropical evergreen forest, Tropical deciduous forest, Thorny bushes, Mountain vegetation and Mangrove forests.
Natural Vegetation of India UPSC Prelims Questions
1. Oak
2. Rhododendron
3. Sandalwood
Select the correct answer using the code given below
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer (d)
of-(2013)
(a) insects and fungi
(b) limited sunlight and paucity of nutrients
(c) water limits and fire
(d) None of the above
Answer (c)
(2013)
1. Hard and waxy leaves
2. Tiny leaves or no leaves
3. Thorns instead of leaves
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1,2 and 3
Answer (d)
(a) African Savannah
(b) Central Asian Steppe
(c) North American Prairie
(d) Siberian Tundra
Answer (b)
(2013)
1. Presence of tall, closely set trees with crowns forming a continuous canopy
2. Coexistence of a large number of species
3. Presence of numerous varieties of epiphytes
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1.2 and 3
Answer (d)
See Also
The Indian Geography

