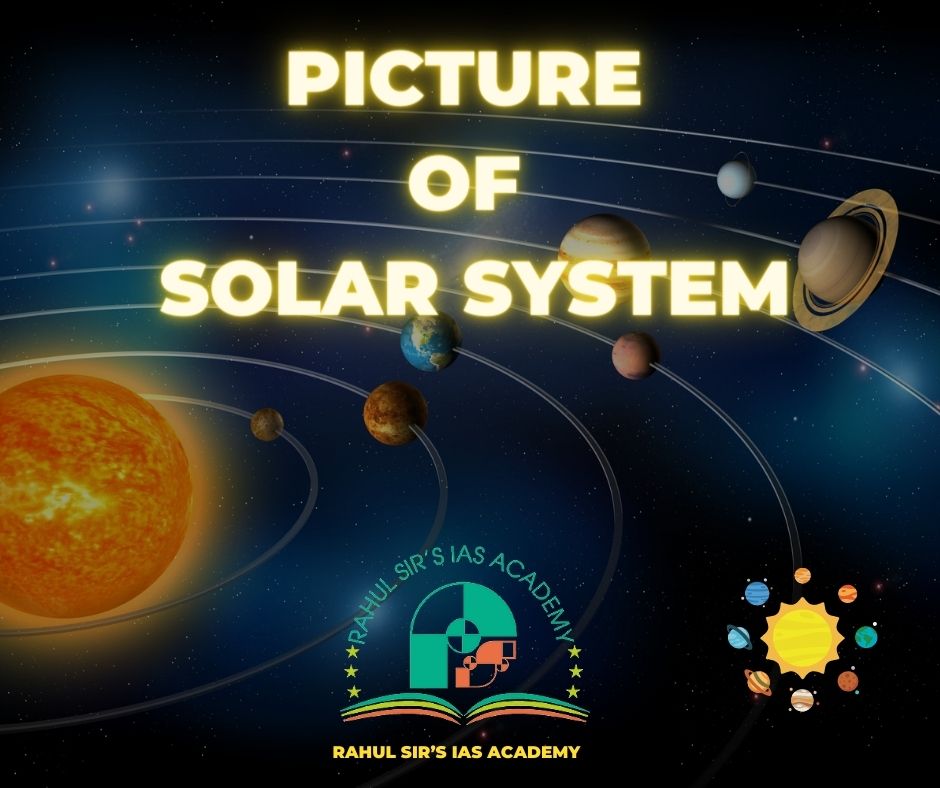
Picture Of Solar System – At A Glance

Major Constituents Of Our Solar System – Picture Of SOLAR SYSTEM
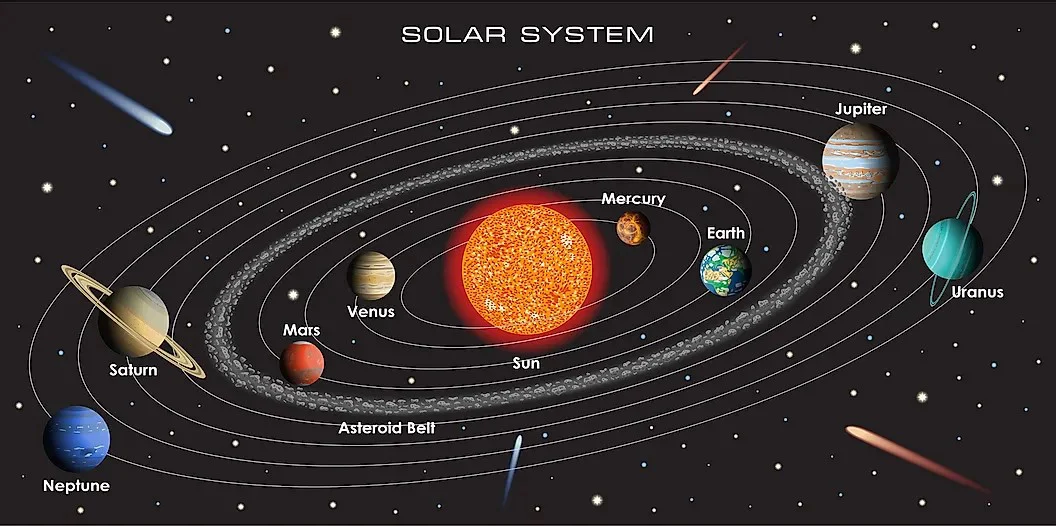
Picture of Solar Solar System
In this article on picture of solar system we shall delve into some of the most salient features of it. At its first glimpse the picture of Solar system appears to be an amazing matrix of planets revolving around the Sun. The picture of solar system is an incredible network of planets and other heavenly bodies revolving around the Sun. The picture of solar system can be studied with Newtonian physics as well as with the help of Einstein’s theory of Relativity. Our solar system is the collection of heavenly bodies that encircle round the sun. It is located on the outer fringes of the Milky Way Galaxy. It includes:
- The sun,
- The Nine planets and their satellites ,
- Asteroids,
- Meteors,
- Comets and
- Drifting particles called interplanetary dust and electrically charged gasses called plasma.
The Sun
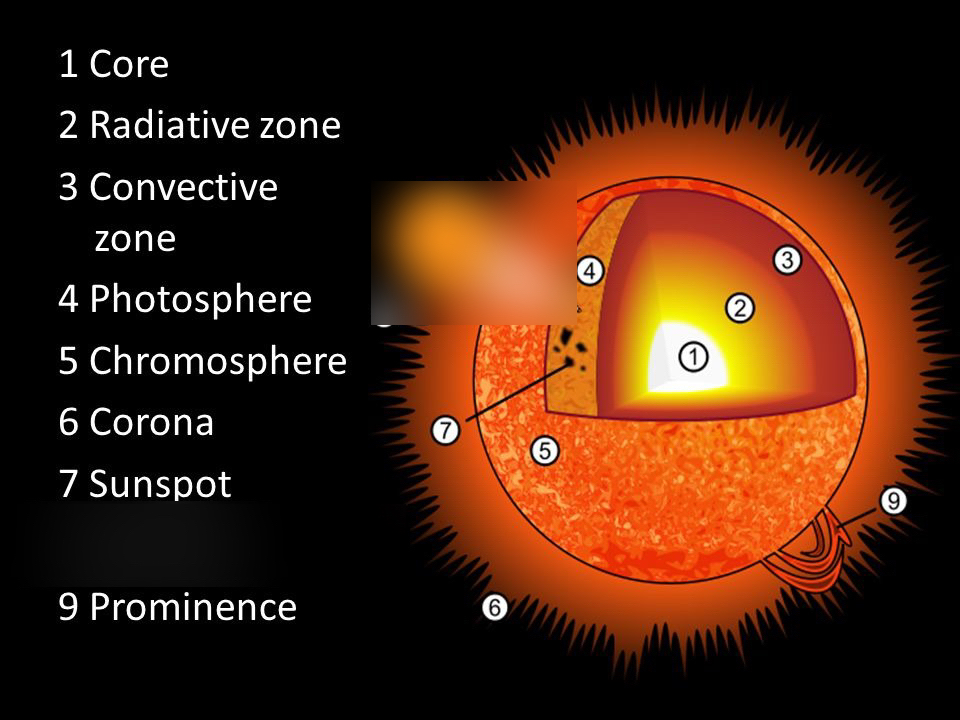
Sun Details
The Sun is one of more than 100 billion stars in the giant spiral galaxy called the Milky Way. It accounts for 85 % mass of the solar system. The gravitational force created by the huge mass of the Sun keeps other objects (planets) traveling around it. The sun continuously gives off energy in several forms – visible light, invisible infrared, ultra-violet, x-rays, gamma rays, radio waves and plasma. The glowing surface of the sun, which is seen, is called ‘photosphere’.
Solar prominence: The sun emits streams of substances mainly hydrogen in all directions. These are called prominence which send huge bouts of incandescent material upward from the sun’s surface. When these eruptions roll out of the atmosphere for many miles, they are seen as solar flares.
Solar winds: President streams of protons blowing out of the corona and sweeping over the whole solar system are called solar winds. They are made up of plasma, ionized gas.
Plages & Sunspot: Changes continuously occur on the surface of the sun . Bright spots called plages and dark spots called sunspot frequently form and disappear. Sunspots appear dark because they are cooler by about 15000 C than the surface of the sun. These sunspots show strong magnetic fields and reach a maximum every eleven years. They affect global atmosphere and climate and interrupt radio communications.
Aurora Borealis/Australis: Aurora Borealis or northern lights and Aurora Australis or southern lights are multi-colored lights that sweep across the sky in weaves and are visible in the Arctic region and Antarctic region respectively. The Earth’s magnetic poles attract the electrified particles coming from the sun. These electrified particles cause gasses in the upper atmosphere, or more appropriately the magnetosphere, to vibrate and glow in colors.
PLANETARY WORLD
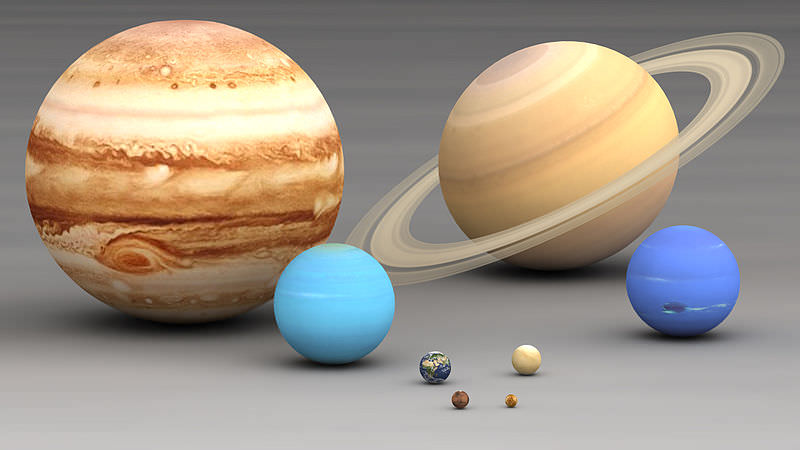
Size Comparison
Under the impact of the sun’s gravitational force, all the nine planets revolve around the sun, in an elliptical orbit . The planets in order from the sun are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto .
- The planets, except Venus and Uranus , also rotate anticlockwise at their axes.
- The planets except Pluto on the basis of their characteristics may be classified into :
- Terrestrial (earth- like ) planets or inner planets which have denser material. Planets in this category are Mercury , Venus , Earth and Mars.
- Jovian planets (Jupiter-like) or outer planets which are gaseous , gigantic with large satellite families and high rotational velocities. These are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
- The largest terrestrial planet is earth while the smallest jovian planet is Neptune.
- The planets in the descending order of their sizes are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Earth, Venus, Mars, Mercury and Pluto.
- Planet Mercury and Venus have no satellites.
- Planet closest to the earth is Venus. After that come Mars, Mercury, and Jupiter.
Mercury
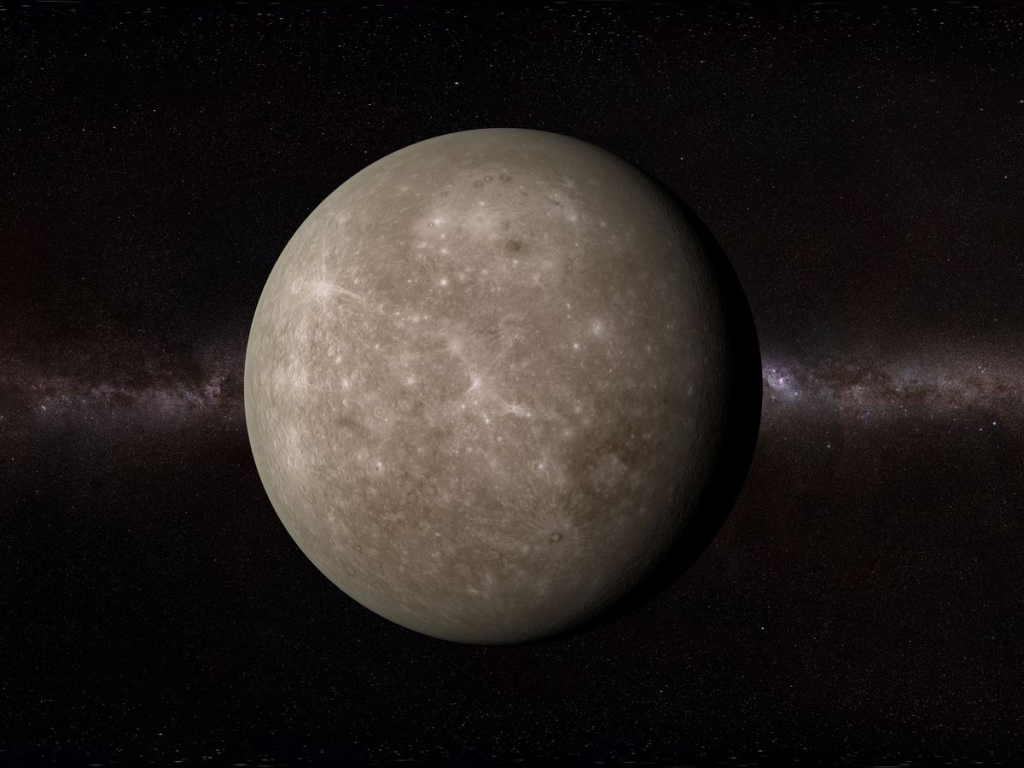

Mercury, the innermost planet, has the fastest orbital motion (48 km/s ) in compliance with Kepler’s laws and the shortest period of revolution, 88 days. This fast speed keeps it from being drawn into the sun’s gravitational field. The planet has a created surface, much like our moon’s and has no atmosphere. It is characterized by the maximum diurnal range of temperature.
More
- Closest planet to the Sun
- No substantial atmosphere
- Extreme temperature variations
- Surface covered in craters and plains
- Distance from the Sun: 57.9 million kilometers (36.0 million miles)
- Inclination of Axis: Virtually no axial tilt
- Speed of Rotation: Slow, with a day lasting about 59 Earth days
- Revolution Period: About 88 Earth days
- Number of Moons: None
- Atmosphere: Extremely thin, primarily composed of trace gases
- Extra: Named after the Roman messenger god, Mercury has a surface scarred by impact craters and expansive plains.
Venus (The Veiled Planet)
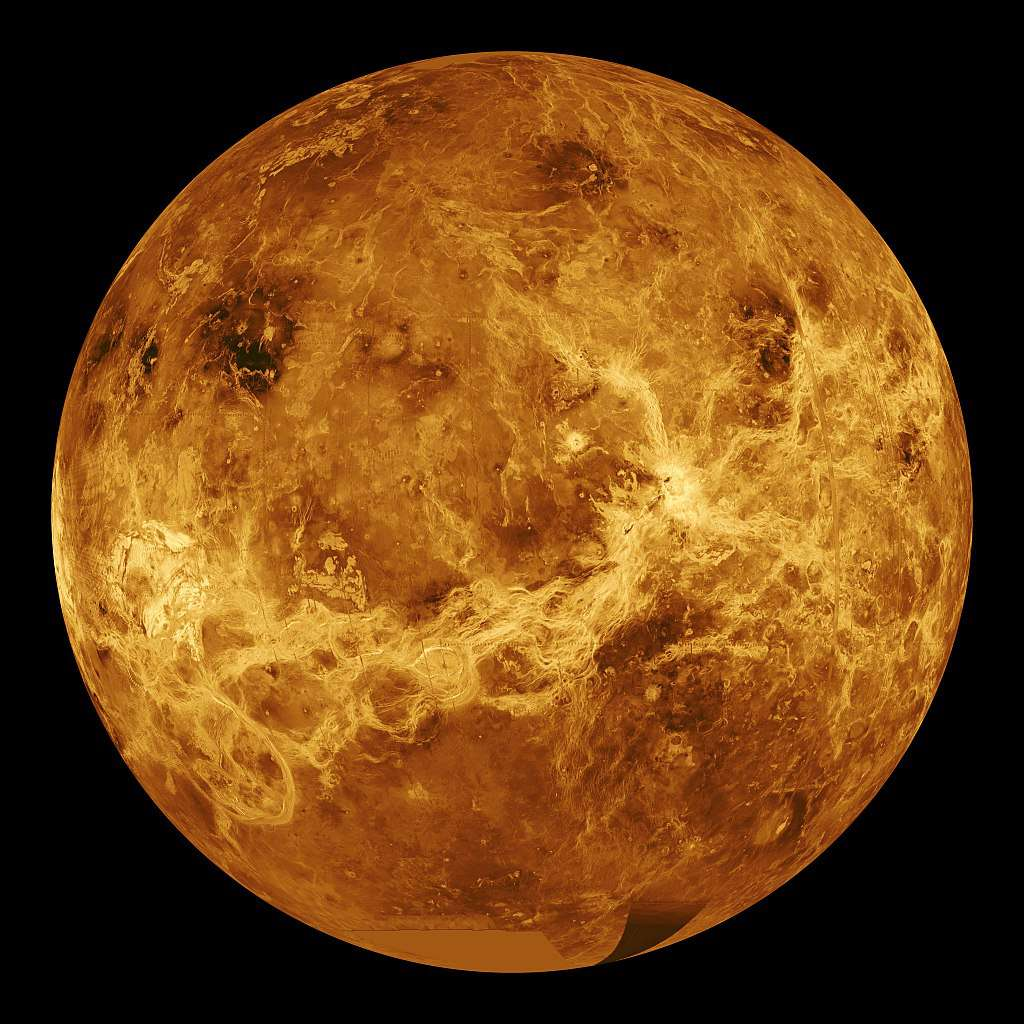

Diameter – 12112 km. Relative mass — 0.820 (earth = 1) polar flattening – 0.0 (% ) Inclination of axis — 177.20 Number of known satellites – 0
Venus, the closest planet to the earth , is also called earth’s twin because of its similar size, density and mass. It is suitably named for the goddess of beauty and love as it is second only to the moon in brilliance in the night sky and is popularly known as Evening star or morning star. Venus is shrouded with a thick cloud cover and its atmosphere consists primarily of carbon di-oxide (90-95 %). The planet is considered as the hottest one and it has the slowest rotational velocity also.
More
- Similar in size and composition to Earth
- Thick, toxic atmosphere of carbon dioxide
- Surface pressure is 92 times that of Earth
- Extremely high temperatures due to the greenhouse effect
- No magnetic field
- Distance from the Sun: 108.2 million kilometers (67.2 million miles)
- Inclination of Axis: Tilted at about 177.4 degrees, nearly upside-down
- Speed of Rotation: Very slow, with a day longer than its year
- Revolution Period: About 225 Earth days
- Number of Moons: None
- Atmosphere: Dense and primarily carbon dioxide with clouds of sulfuric acid
- Extra: Venus experiences a superheated greenhouse effect, making it the hottest planet in our solar system.
Earth (The Blue Planet)
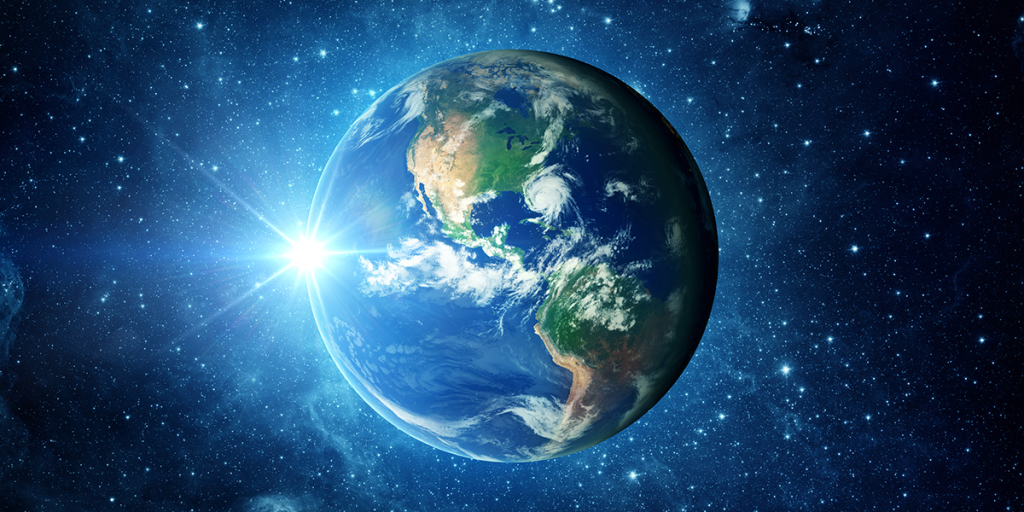

Diameter – 12742, Inclination of axis : 230 27’, polar flattening : 0.3 %
The earth, the densest and fifth largest planet of the solar system, is having such temperature ranges that water can exit here as solid, liquid and gas. This has made possible the evolution of life forms on this planet.
More
- Third planet from the Sun
- Only known planet to support life
- Abundant water, diverse ecosystems
- Atmosphere with oxygen and nitrogen
- Complex geological activity
- Distance from the Sun: 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles)
- Inclination of Axis: Tilted at about 23.5 degrees
- Speed of Rotation: About 1670 kilometers per hour (1037 miles per hour) at the equator
- Revolution Period: About 365.25 days
- Number of Moons: One (the Moon)
- Atmosphere: Rich in nitrogen and oxygen, supporting a variety of life
- Extra: Earth is the only planet known to support a diverse range of life.
Mars – Picture Of Solar System
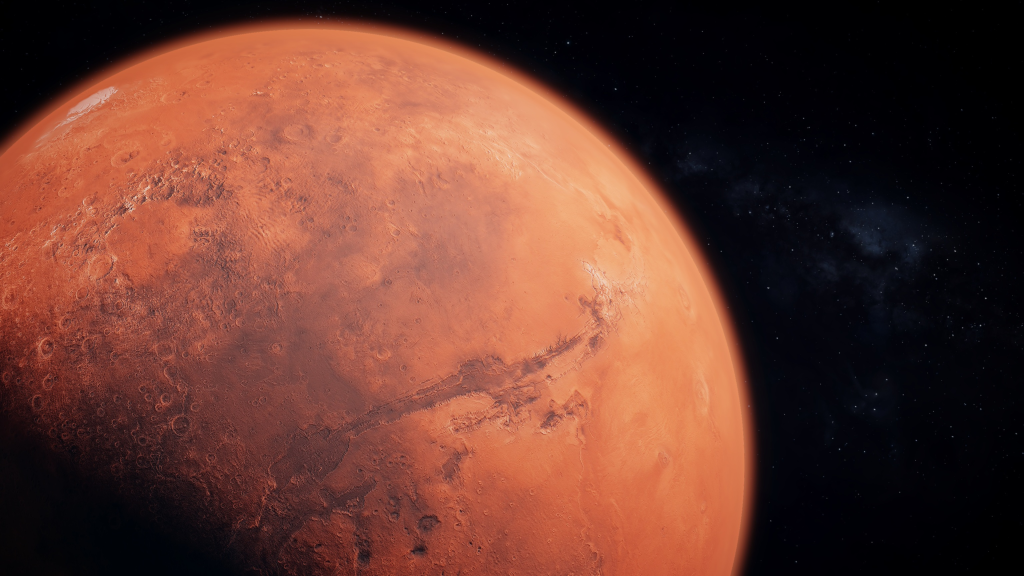

Mars appearing as a reddish ball, has evoked greater interest than any other planet because of presumption of possibility of life on it. The angle of inclination and period of rotation is nearly the same as that of earth. Hence Mars has seasons much like the earth. There is evidence not only of stream action here but of catastrophic flooding too.
More
- The “Red Planet”
- Thin atmosphere with carbon dioxide
- Polar ice caps
- Evidence of past water flows
- Ongoing missions for potential colonization
- Distance from the Sun: 227.9 million kilometers (141.6 million miles)
- Inclination of Axis: Tilted at about 25.2 degrees
- Speed of Rotation: Similar to Earth, with a day lasting about 24.6 hours
- Revolution Period: About 687 Earth days
- Number of Moons: Two (Phobos and Deimos)
- Atmosphere: Thin carbon dioxide atmosphere
- Extra: Mars has the largest volcano in the solar system, Olympus Mons, and a vast canyon, Valles Marineris.
Jupiter (The Giant Planet) – Picture Of Solar System
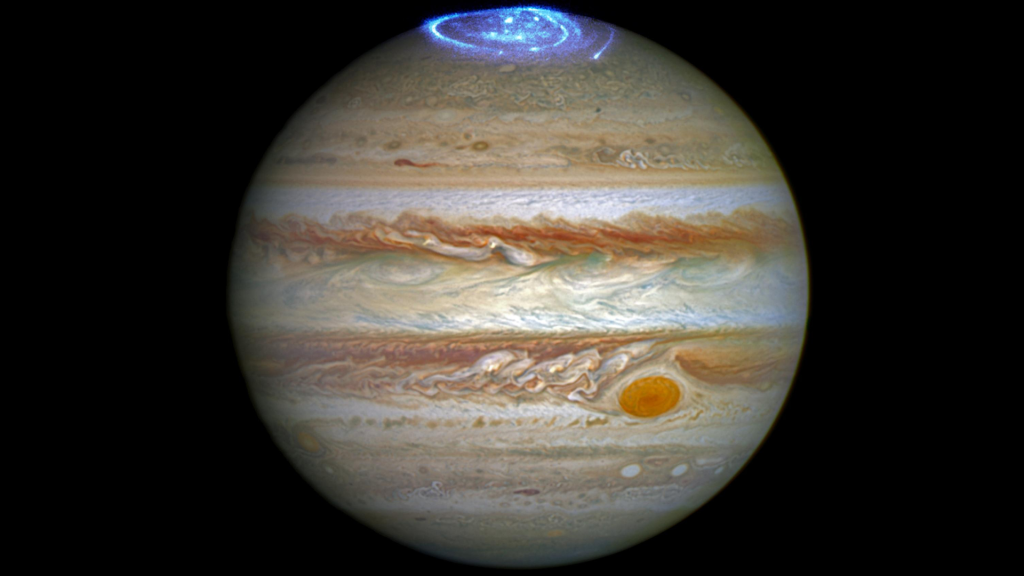

Diameter – 1,43,000 km , Relative mass – 318.0 ( Earth = 1), Polar flattening – 6.5 % , Inclination of axis – 305.’
This giant planet is 1300 times greater than the earth’s but it is composed mostly of gas and liquid swirling in complex patterns. Its atmosphere consists largely of hydrogen and helium which accounts for the low density of the planet. Jupiter has the fastest rotational velocity among the planets. Since, Jupiter has no solid surface hence there is no record of geologic history. Its satellites are, however, solid bodies. The largest of its over 100 known satellites are Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto which are called Galilean satellites. Ganymede is the largest satellite of the solar system and is almost the size of earth.
More
- Largest planet in the solar system
- Mostly composed of hydrogen and helium
- Strongest magnetic field
- Dozens of moons, including the Galilean moons
- Great Red Spot, a massive storm
- Distance from the Sun: 778.3 million kilometers (483.8 million miles)
- Inclination of Axis: Tilted at about 3.1 degrees
- Speed of Rotation: Very fast, completing a day in less than 10 hours
- Revolution Period: About 11.9 Earth years
- Number of Moons: Over 80 known, including the four Galilean moons
- Atmosphere: Primarily hydrogen and helium, with colorful cloud bands
- Extra: Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is a massive, long-lived storm.
Saturn ( The Ringed Planet )

Diameter – 1, 21,000 km Relative mass – 95.20 (Earth =1 ) Polar flattening – 10.5% Inclination of axis – 26044’
The unique feature of this second largest planet is its spectacular system of seven rings, identified by the letter ‘A’ to ‘G’ ( though not in an alphabetical order). These rings, discovered by Galileo, are made up of individual moonlets of varying sizes. Saturn has the biggest family of satellites, a total of eighteen or more. Titan, the largest satellite , is the only one in the solar system with an atmosphere of its own. Saturn has the least density among all the planets.
More
- Known for its stunning ring system
- Mostly composed of hydrogen and helium
- Extensive moon system, including Titan
- Unique hexagonal cloud pattern at its north pole
- Distance from the Sun: 1.4 billion kilometers (886 million miles)
- Inclination of Axis: Tilted at about 26.7 degrees
- Speed of Rotation: A day lasts about 10.7 hours
- Revolution Period: About 29.5 Earth years
- Number of Moons: Over 80 known, with its rings made up of numerous small particles
- Atmosphere: Predominantly hydrogen and helium
- Extra: Saturn’s rings are its most distinctive feature, consisting of ice and rock particles.
Uranus (The Green Planet) – Picture Of Solar System
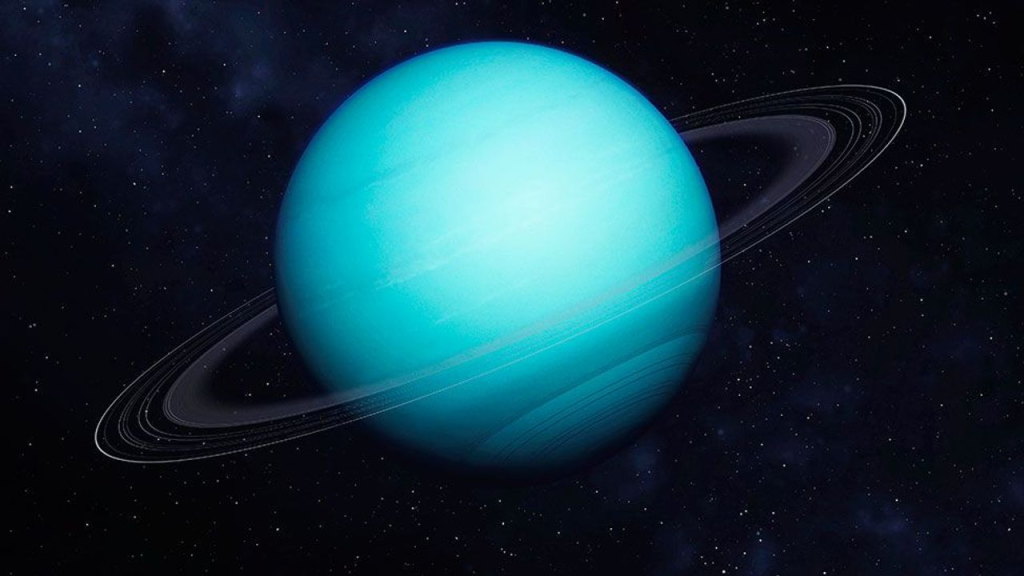

Diameter — 47,000 km, Relative mass – 14.6 ( Earth = 1 ), Polar flattening – 7.0 % , Inclination of axis — 97055’, Number of satellites – 5.
This chilly methane planet is unique in the sense that its axis of rotation lies only eight degrees from its orbital plane. Therefore its rotational motion has the appearance of a spinning ball, unlike other planets which spin on their axis.
More
- Tilted on its side, making it appear to roll along its orbit
- Blue-green color due to methane in the atmosphere
- Rings are faint and narrow
- Several moons, with Miranda known for its unique surface features
- Distance from the Sun: 2.9 billion kilometers (1.8 billion miles)
- Inclination of Axis: Tilted at about 97.8 degrees, almost perpendicular
- Speed of Rotation: A day lasts about 17.2 hours
- Revolution Period: About 84 Earth years
- Number of Moons: 27 known
- Atmosphere: Predominantly hydrogen and helium, with traces of methane
- Extra: Uranus rotates on its side, possibly due to a past collision.
Neptune – Picture Of Solar System
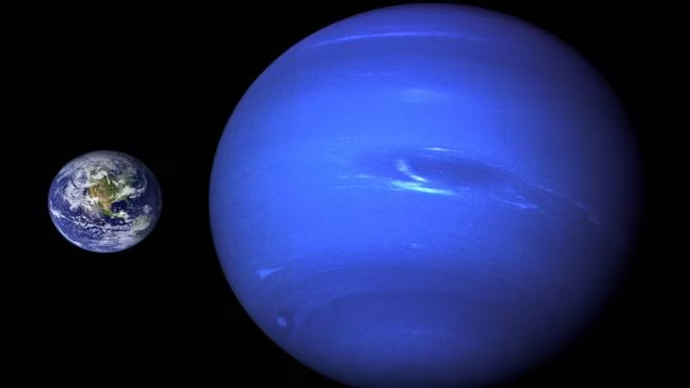
Diameter – 45,000 km Relative mass – 17.3 Inclination of axis – 28048’.
Uranus and Neptune come most closely if any two planets in the solar system can be considered twins. A part fresh being, attributable to the methane in their atmosphere. Neptune’s atmosphere contains an earth sized blemish called the Great Dark Spot. It has eight tiny satellites, ton being the largest.
More
- Dark, stormy atmosphere with high winds
- Similar in composition to Uranus
- Active storms, including the Great Dark Spot
- Numerous moons, including Triton with geysers
- Distance from the Sun: 4.5 billion kilometers (2.8 billion miles)
- Inclination of Axis: Tilted at about 28.3 degrees
- Speed of Rotation: A day lasts about 16.1 hours
- Revolution Period: About 164.8 Earth years
- Number of Moons: 14 known
- Atmosphere: Primarily hydrogen and helium, with traces of methane
- Extra: Neptune’s atmosphere is known for its dynamic and fast-moving storms.
Pluto (The planet X) – Why Excluded From Our Solar System?
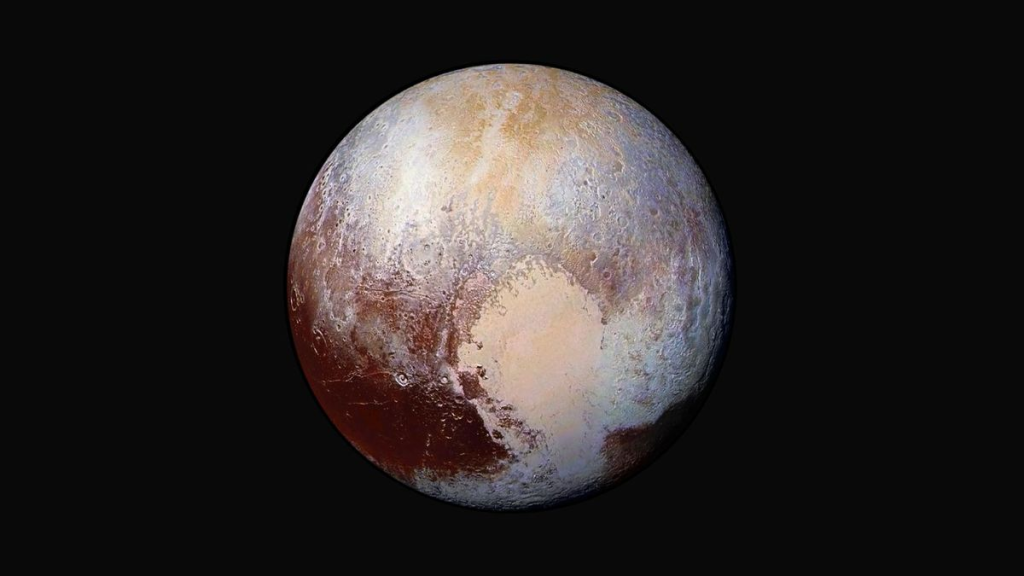

Diameter – 2,330 km surface temperature – 2300 C Number of satellites –1
It’s not included in our Solar system anymore for a variety of reasons. The farthest, smallest, darkest and the coldest planet, Pluto was first discovered by P. Lowell only by mathematical calculations who accordingly named it as planet X. Its satellite, Charon, is nearly half its size due to which Pluto appears like a bi-planet. NASA using an improved telescope has shown that Pluto is shrouded in frozen nitrogen but methane as once thought. The unique feature of Pluto is its orbit – the most eccentric one: at its closest approach to the sun and the farthest, it is 4.4 and 7.3 billion kilometers away respectively. Due to this eccentricity, Neptune becomes the farthest planet whenever Pluto’s path crosses inside Neptune’s. This was the situation between 1979 to 1999. And now it is Pluto’s turn again for the next 248 years.
More
- Former ninth planet, reclassified as a dwarf planet
- Icy, rocky body in the Kuiper Belt
- Charon is its largest moon
- New Horizons mission provided close-up images
- Distance from the Sun: Varies from about 4.4 billion to 7.4 billion kilometers (2.7 billion to 4.6 billion miles)
- Inclination of Axis: Tilted at about 119.6 degrees, lying nearly on its side
- Speed of Rotation: Slow, with a day lasting about 6.4 Earth days
- Revolution Period: About 248 Earth years
- Number of Moons: Five known, including Charon
- Atmosphere: Thin nitrogen and methane atmosphere
- Extra: Pluto is part of the Kuiper Belt, a region of icy objects beyond Neptune.
Conclusion On Picture Of Solar System
Thus, the captivating tapestry of the solar system, with its diverse array of planets, moons, asteroids, and comets, stands as a testament to the awe-inspiring beauty and complexity of the universe. Through the lens of science and the artistry of imagination, we have embarked on a visual journey that has unveiled the wonders of our celestial neighborhood. From the fiery brilliance of the Sun to the icy realms of the outer planets, every image captured and every discovery made have deepened our understanding of the solar system’s intricate dance.
Moreover, these images not only ignite our curiosity but also inspire a sense of unity and responsibility towards our fragile planet Earth. In the grand tapestry of the cosmos, our home shines as a unique oasis, reminding us of the preciousness of our world and the importance of preserving it for future generations.
As we continue to explore and study the solar system, we can look forward to even more breath taking images and ground breaking discoveries. Whether through robotic spacecraft or the aspirations of human exploration, the picture of the solar system will continue to evolve, providing us with fresh perspectives on our place in the universe. It is a picture that invites us to dream, to explore, and to embrace the boundless wonder of the cosmos that surrounds us.
See Also
Facts About Universe – In A Nutshell
FAQs On Picture Of Solar System
Pluto, due to its far distance from the Sun.
It is a collection of celestial bodies that comprises Sun, 8 Planets with their moons, Asteroids and comets.

