
World Climate Zones Maps
In this article we’ll learn about the various world climate zones maps as there is a huge diversity in the world in terms of Climate. The words climate and weather are many times used interchangeably in common parlance but in reality they are quite different. Whereas climate is the long-term pattern of weather in a particular area, weather on the other hand can change on a hour-to-hour, day-to-day, month-to-month or even year-to-year basis. The weather patterns of a region are usually tracked for at least 30 years time span.
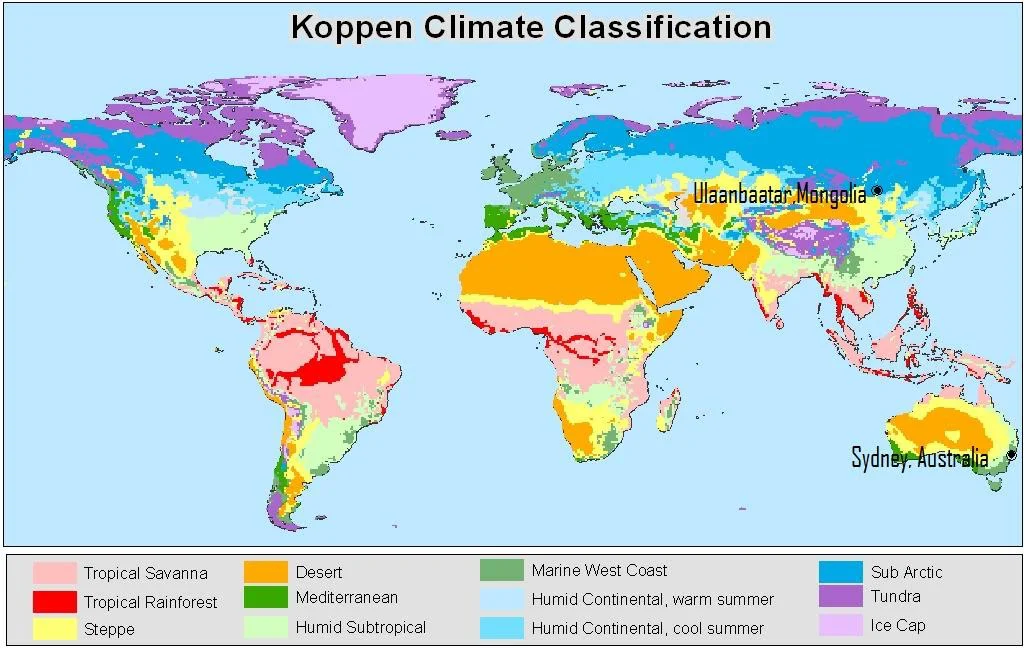
The most elaborate and extensive climate classification system of world climate zones was given by Wladimir Koppen, who was a Botanist by profession. Koppen’s main climate groups are based on what types of vegetation that grow in a given climate classification region. Along with this the system can also be used for the analysis of ecosystem conditions and to identify the main types of vegetation within climates. Hence because of the link between climate and the plant life of a given region, Koppen’s system is useful in predicting future changes in plant life within that region.
Major Components Of Climate – World Climate Zones Maps
- Atmosphere : The movement of air and gasses radically influence the climate patterns of the world. These also include the man made factors.
- Hydrosphere: The movement of ocean currents and variations in temperature and salinity, occur at much slower rates than changes to the atmosphere.
- Cryosphere: It is the icy part of our ecosystem. This is another generally consistent part of the climate system. Ice sheets and glaciers reflect sunlight, and the thermal conductivity of ice and permafrost profoundly influences temperature. It also regulates the Thermo-Haline circulation.
- Biosphere: The biosphere, the sum total of living things on Earth, profoundly influences climate. Vegetation influences climate by helping determine how the Sun’s energy is used on Earth. The abundance of plants and the type of land cover (such as soil, sand, or asphalt) impacts evaporation and ambient temperature. By means of Photosynthesis, plants contribute to the regulation of flow of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere. Forests and oceans serve as “carbon sinks” that have a cooling impact on climate. Living organisms alter the landscape, through both natural growth and created structures such as burrows, dams, and mounds. These altered landscapes can influence weather patterns such as wind, erosion, and even temperature.
Other Factors
a) Latitude
b) Proximity to the ocean
c) Proximity to fresh water
d) Landscape
e) Land use patterns
World Climate Zones Maps
The climatic regions of the world or the world climate zones, are divided on the basis of definite temperature and rainfall patterns. The major climatic types and their main characteristics have been presented here:
Equatorial Climate/Tropical Rain Forest
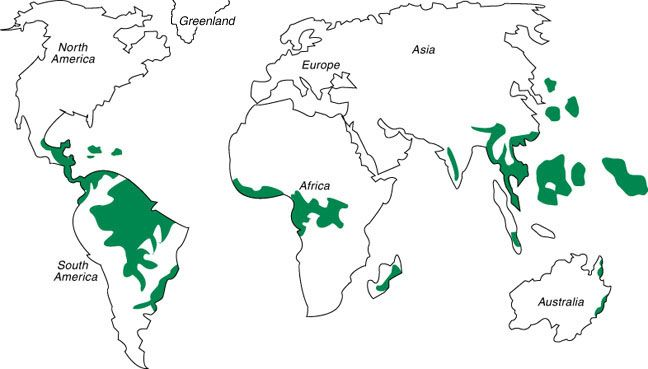
Tropical Rain Forest
- Prevails mainly between 100 N and 100 S of equator.
- Found in the Amazon lowlands ( S America), Congo Basin (Africa), Madagascar and East Indies (from Sumatra to New Guinea).
- Rainfall mostly convection occurs throughout the year.
- Annual rainfall is about 200 cm, though some regions get heavier rains.
- Climate is consistently moist with no month recording less than 6 cm of rainfall.
- Mean monthly temperature ranges between 240-270 C.
- Annual ranges of temperature commonly less than 20 to 30 C.
- Diurnal range of temperature is more, i.e. 60 to 80 C.
- A region of great biodiversity – abundance of flora & Fauna.
- Diseases & insects, harsh climate and dense forests pose hindrance to economic development.
Tropical Monsoon Climate
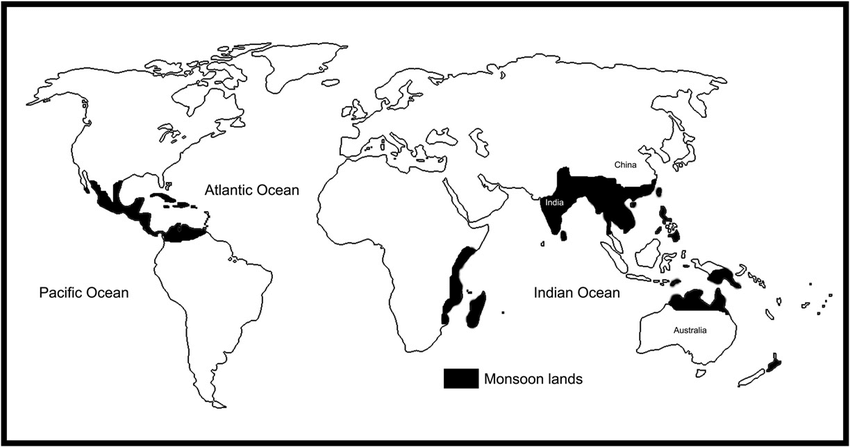
Map of Tropical Monsoon Climate
- It is found Within the tropics in the eastern sides of the continents of the world climate zones maps.
- Spreads over south, south-east and east Asia (India, Myanmar, South China ) and northern /Australia.
- Dominant characteristics-complete reversal of prevailing wind direction from season to season.
- Average annual rainfall is about 150 cm.
- Rainfall is highly erratic, mainly in the summer season.
- Average temperature of summer is 300 C and of winter is 150 C.
- A distinct dry season ( in winter) one or more months with rain less than 6 cm
- Forests are rich in Sal, Teak, Shisham & Bamboo.
Savanna / Tropical Grassland / Sudan Climate
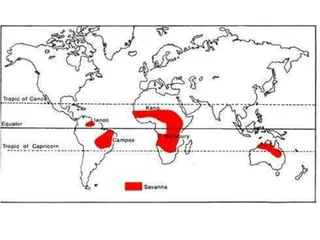
Tropical Grassland / Savanna / Sudan Climate
- Found between 50 to 150 north and south of the world climate zones maps.
- Transitional zone between the equatorial & monsoon on the one hand and arid & semi-arid climates on the other.
- Found in Africa ( north & south of equatorial belt) , East central south America ( Llanos in Colombia high-land Campos in Brazil), Northern Australia and some parts of India ( man-induced).
- High temperature throughout the year.
- Average annual temperature is more than 250 C.
- High summer temperature around 32-C while winter temperature is about 210 C.
- Annual range of temperature 110 C.
- A Distinct dry season in winter when the region comes under the influence of trade winds.
- Average annual rainfall around 75 cm, rainfall mainly in summer (mainly of convectional type).
- Natural vegetation comprises toll grasses with scattered trees, called ‘Parkland Vegetation’.
Dry tropical (Desert) climate
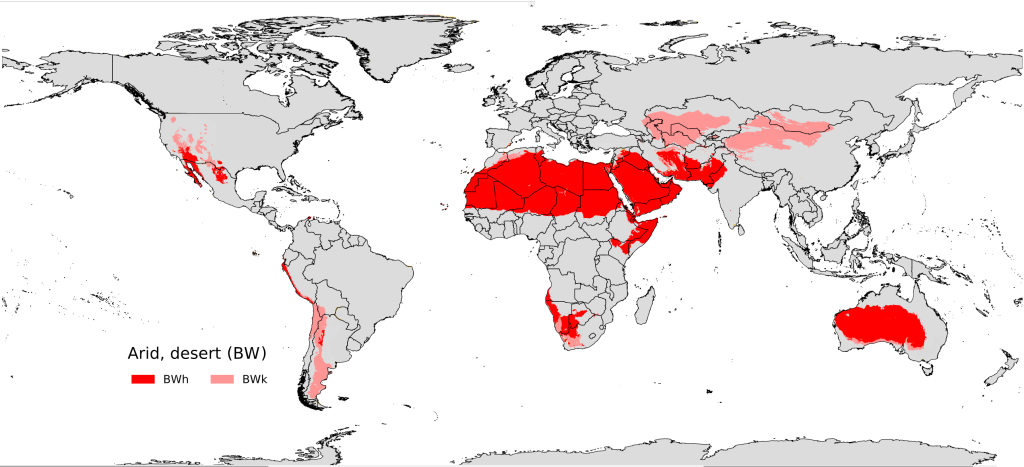
Dry tropical (Desert) climate
- Found on the western margins of continents along the tropic of cancer and tropic of Capricorn in the world climate zones maps.
- Chief regions are the Sahara desert ( Africa) , Great Australian desert, Arabian, Iranian & that desert in Asia, Kalahari & Namib desert (Africa), Mojave desert in North America and Atacama desert in South America.
- The main cause of aridity is their location in the subtropical high pressure belt and the effect of dry offshore trade winds on the western margins of continents.
- Mean summer temperature around 300 C & mean winter temperature about 100 C.
- Diurnal temperature ranges are very high from 150 C to 400 C.
- Highest temperatures have been recorded in this climate e.g. 58.70 C in all of Al Azizia (Libya), 580 C in death valley, 520 C in Jacobabad ( Pakistan) of thar.
- Annual rainfall is very low, about 12cm, rainfall highly variable.
- Vegetation is of Xerophytic type.
Warm Temperate Western Margin / Mediterranean Climate
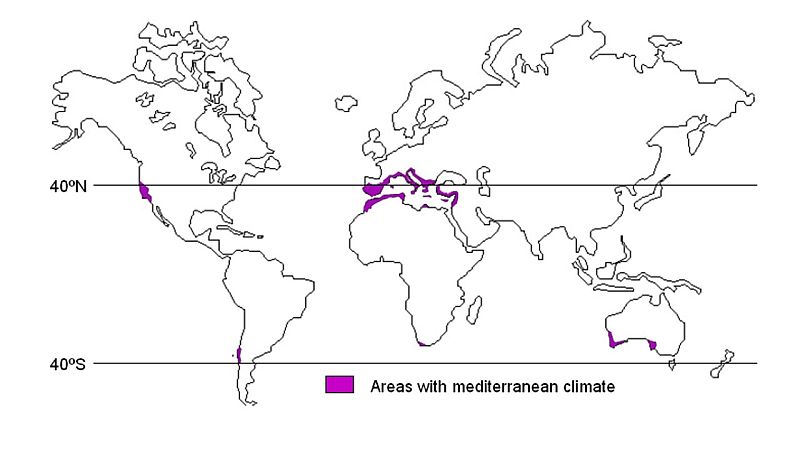
Mediterranean Climate
- Found between 300-450 latitudes in both hemispheres on the western side of each continent.
- Its typical areas are around the shores of Mediterranean sea , south-west Africa (cape region), Central Chile, Central California and south-west and southern Australia ( Adelaide to Melbourne).
- Pre-dominant characteristics are dry summer and mild-moist winter.
- Summer is dry because trade winds blow offshore.
- But in winter the region comes under the influence of onshore westerlies due to shifting of the pressure belts towards equator. These westerlies bring winter rainfall here.
- Annual rainfall varies between 50 and 75 cm.
- Summer temperature ranges between 200-270 C while winter temperatures are 40 to 100.
- This climate experiences hot dusty wind of Sirocco and cold winds of mistral (France) and Bora (Yugoslavia).
- This climate region is noted for its orchard farming of citrus fruits , especially viticulture ( grape farming)
Temperate Continental (Steppe) / Warm Temperate Interior Climate
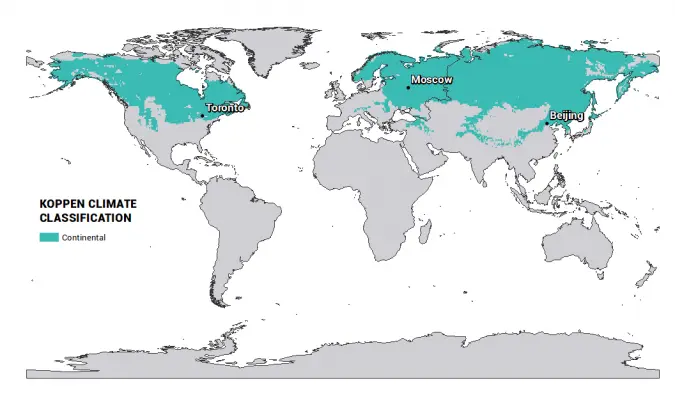
Temperate Continental
- Located in the interiors of the continents due to which they do not get sufficient rainfall from the westerlies.
- Spreads over the temperate grassland regions of the world, i.e. Steppes of Eurasia, Prairies of North America, Velds of South Africa , Pampas of South America, Downs of Australia, Canterbury grassland of New Zealand and Pustaz of Hungary.
- Warm summer with about 200 C temperature and cold winter with about 50-100 C.
- Average annual rainfall ranges between 25 cm-75 cm
- Rainfall mostly in summer.
- Grasslands are practically treeless.
Dry Mid-Latitude / Temperate Desert Climate – World Climate Zones Maps
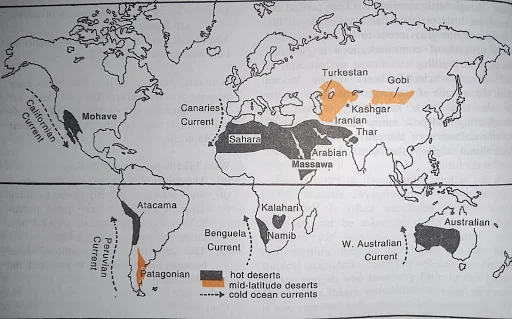
Temperate Desert Climate
- Found between 300– 450 latitudes in the interiors of continents.
- Main areas are Gobi, Tibet, Mongolia and Turkistan in central Asia, and Patagonia in South America.
- Diurnal range of temperature is up to 500 C.
- Annual range of temperature is low ( high)
- Rainfall is scanty, about 12 cm.
- Main cause of aridity is interior location or intermontane location.
Warm Temperate Eastern Margin / China Type Climate – World Climate Zones Maps
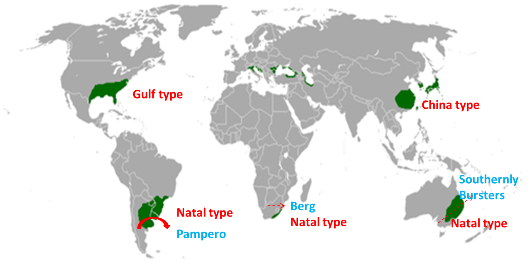
China Type Climate
- Found on the eastern margin of continents between 250-450 North and South.
- Chief regions are Eastern & Central China, S.E. America and the south eastern part of Africa and Australia, S. Brazil & S. Japan.
- Average summer temperature is 260 C while average winter temperature is 130C.
- 70% or more of the mean annual rainfall in warmer six months.
- Warmest month of summer has at least 10 times the precipitation of the driest month of winter. Average annual rainfall is 100 cm.
- Pampero (Argentina) & southerly Buster (Australia) are cold local winds blowing in this climate.
- Tropical cyclones winds e.g. Typhons (S. China) & Hurricanes (S.E. USA) are common in summer.
- Normally mixed forest of coniferous & broad leaved forests is found.
British Type / Cool Temperate Western Margin / West European Climate
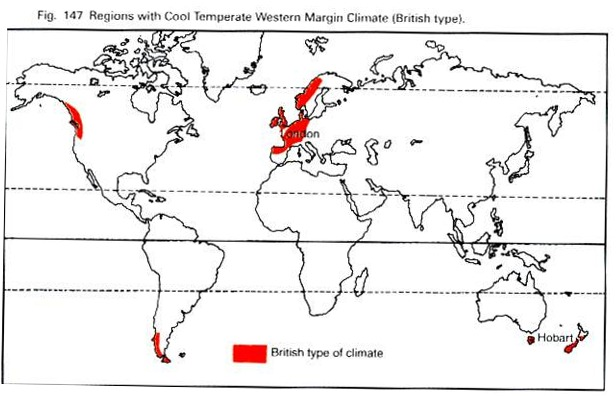
Cool Temperate Western Margin
- Prevails along the western margins of continents between 450-600 latitudes in both hemispheres.
- Representative areas are N-W Europe, western Canada, Southern Chile, and Southern Island of New-Zealand & Tasmania.
- Rainfall Throughout the year, but more in winter.
- The region comes under the permanent westerly winds which blow from the oceans keeping the moist throughout the year.
- Total annual rainfall-100 cm, rainfall mainly cyclonic.
- Mean winter temperature is 50 C while that of summer is 150 C
- The annual temperature ranges are not high, i.e. 80 C to 110 C caused by the combined effect of warm ocean currents (North Atlantic & N. Pacific Drifts) and winds.
- Both deciduous & Coniferous forests are found.
Cool Temperate Eastern Margin / Laurentian Climate – World Climate Zones Maps
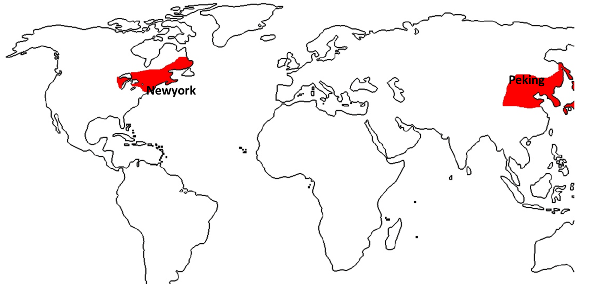
Laurentian Climate
- Found on the eastern margins of continents between 450-650 latitudes.
- Best developed in N.E. USA (New England), Eastern Canada (St. Lawrence valley), Northern China , Manchuria, Korea & Northern Japan.
- The summer temperature ranges from -150 to 240 C while winter temperature ranges from -90 to -70C.
- Annual temperature range is high compared to western margin.
- Annual rainfall is 75 cm, throughout the year, evenly distributed.
- Fall of temperature in winter due to cold winds blowing from the interior.
- Mixed forest of coniferous & deciduous trees.
Cool Temperate Continental / Taiga Climate – World Climate Zones Maps
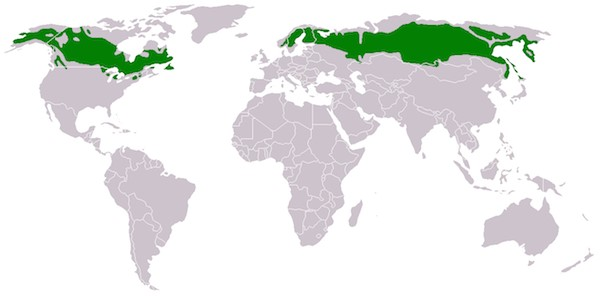
Taiga Climate
- Extends from 450 to 700 latitudes in the northern hemisphere.
- From Alaska to Newfoundland in North America and from Norway to Kamchatka in Eurasia.
- Greatest annual range of temperature of over 550 C is found here.
- The summer temperature is around 150 to 200 while winter temperature ranges from -340 C in Canada to 450 C in parts of CIS.
- Summer is short ( 4-5 months) while winters are long.
- Annual rainfall is 25-50 cm, mostly in summer.
- This climate is distinct for its evergreen coniferous forest or Boreal forest Biome.
Tundra Climate – World Climate Zones Maps
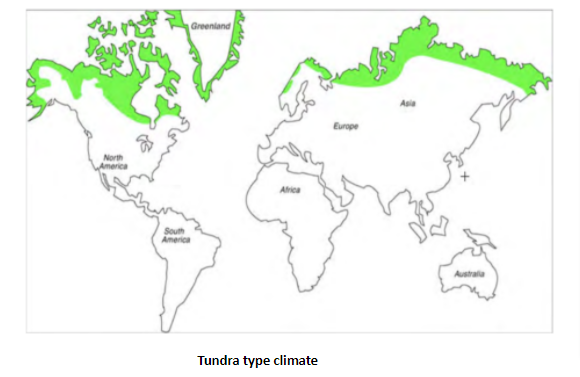
Tundra Climate
- North of 700 latitudes in North America & Eurasia, coastal tract of Iceland & Greenland.
- Warmest month temperature is below 100 C but more than 00 C, average annual temperature is -120 C , annual range of temperature is 390 to 500 C.
- Mean annual precipitation, mostly in the form of snowfall, is below 40 cm.
- Vegetation comprises lichens & mosses supported by characteristic Lithosols of tundra.
Highland Climate – World Climate Zones Maps
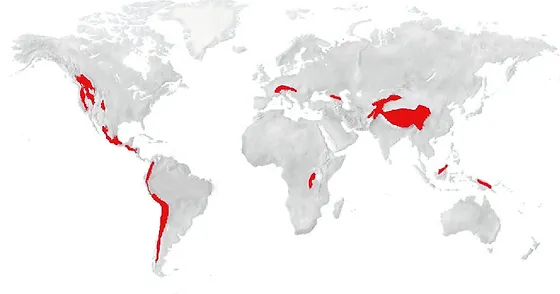
- All the mountain regions of the world are above 1500 meter height.
- Temperature decreases with altitude, therefore there is a vertical zonation of climate from tropical to ice cap type.
- Rainfall on windward slope, leeward side.
Conclusion – World Climate Zones Maps
On the whole there is a vast diversity in the World Climate Zones maps. This is due to a variety of reasons, the primary one being the inclination of Earth’s axis on the plane of the elliptic. The Sun’s rays are never uniformly distributed on the entire surface of the earth. Earth receives direct Sun rays in a band that stretches between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. Thus the Sun rays are direct on the equator twice a year. Due to this there is a variation in climate all over the world. Other reasons for various climate zones are ocean currents, topography and variation in landmass.
See Also
The Atmosphere – Composition and structure
OUR SOLAR SYSTEM – At A Glance
FAQs
Broadly there are 5 world climate zones namely – Tropical, Temperate, Equatorial, Tundra and Highland. Of these Tropical and Temperate zones have a few sub categories.
USA has all the climatic zones including the sub zones. India also has the 5 broad zones but does not have all the sub categories.

